Reading in a File Thats Already Created and Saving Into C Drive in Java
Java: File Input and Output
Introduction
When data items are stored in a computer system, they can be stored for varying periods of time—temporarily or permanently.
- Temporary storage is usually chosen computer retentivity or random access memory (RAM). When you write a Java programme that stores a value in a variable, you are using temporary storage; the value you store is lost when the program ends or the computer loses ability. This type of storage is volatile.
- Permanent storage, on the other mitt, is non lost when a computer loses power; it is nonvolatile. When you write a Coffee plan and save it to a deejay, you are using permanent storage.
Files exist on permanent storage devices, such as hard disks, Zip disks, USB drives, reels or cassettes of magnetic record, and meaty discs .Computer files are the electronic equivalent of paper files often stored in file cabinets in offices.
When yous work with stored files in an awarding, you typically perform all or some of the following tasks:
- Determining whether and where a file exists
- Opening a file
- Reading data from a file
- Writing information to a file
- Closing a file
USING THE File Form
You can use Coffee's File grade to gather file data, such as its size, its nearly recent modification engagement, and whether the file even exists. You must include the post-obit argument to use the File form:
import java.io.File;
The java.io package contains all the classes you utilise in file processing, so it is usually easiest to import the entire packet using the wildcard * graphic symbol, every bit follows:
import java.io.*;
The File grade is a subclass of the Object class. Yous can create a File object using a constructor that includes a filename as its argument, for example, you make the following statement when Data.txt is a file on the project root folder:
File fileName = new File("Data.txt"); Below is the list of some of of import File grade methods with purpose and method signature
| Method name/Signature | Purpose |
|---|---|
| boolean canRead() | Returns true if a file is readable |
| boolean canWrite() | Returns true if a file is writable |
| boolean exists() | Returns true if file exists |
| String getName() | Returns file name |
| Cord getPath() | Returns the file'southward path |
| String getParent() | Returns the name of the folder in which the file tin be found |
| long length() | Returns the file's size |
| long lastModified() | Returns the time the file was last modified; this time is system dependent and should exist used merely for comparison with other files' times, non every bit an absolute time |
| boolean isDirectory( ) | When you create a File object and information technology is a directory, the isDirectory( ) method will render true. |
Allow's understand these method's implementation with help of java program. In the main()method, a File object named myFile is declared. The String passed to the constructor is "SomeData.txt", which is the stored file'south system name. In other words, although SomeData.txt might be the name of a stored file when the operating system refers to it, the file is known as myFile inside the application. Nosotros need to create Information.txt file in project root directory else we will get a message saying "File does not exist".
Java Code: Become to the editor
import java.io.File; public class FileClassMethods { public static void chief(String[] args) { File myFile = new File("Information.txt"); if (myFile.exists()) { System.out.println(myFile.getName() + " exists"); System.out.println("The file is " + myFile.length() + " bytes long"); if (myFile.canRead()) System.out.println(" ok to read"); else System.out.println(" non ok to read"); if (myFile.canWrite()) System.out.println(" ok to write"); else System.out.println(" non ok to write"); System.out.println("path: " +myFile.getAbsolutePath()); Organization.out.println("File Name: "+ myFile.getName()); System.out.println("File Size: "+ myFile.length() + " bytes"); } else System.out.println("File does not be"); } } Output:
If file is not available in project root binder.
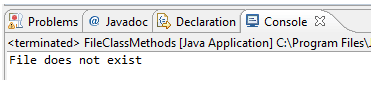
when the file is nowadays:
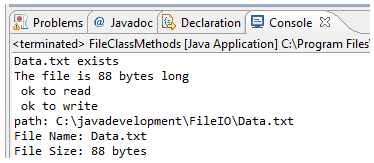
Handling Exceptions
Several exceptions in the java.io parcel might occur when you are working with files and streams.
- A FileNotFound exception occurs when you try to create a stream or file object using a file that couldn't be located.
- An EOFException indicates that the end of a file has been reached unexpectedly equally data was beingness read from the file through an input stream.
These exceptions are subclasses of IOException. One way to deal with all of them is to enclose all input and output statements in a endeavour-take hold of cake that catches IOException objects. Call the exception'southward toString() or getMessage() methods in the catch block to notice out more nigh the problem
Summary
- All real life application generates lots of information which need to be referred at a later on stage. This requirement is accomplished using File storage on a permanent storage device like a disk drive, CD ROM, pen bulldoze etc.
- Java provides a library of classes to access this permanently stored information on files called FileIO or java.io. * Package.
- java.io.File class provides some of the very useful utility methods like permission checking, file size checking, absolute path checking etc.
Java Lawmaking Editor:
Previous: String buffer form and string architect class
Next:Reading file
Source: https://www.w3resource.com/java-tutorial/file-input-and-output.php
0 Response to "Reading in a File Thats Already Created and Saving Into C Drive in Java"
Post a Comment